Explain How Different Enzymes Assist in the Replication of Dna.
The two separated strands will act. Elongates DNA strand by adding.
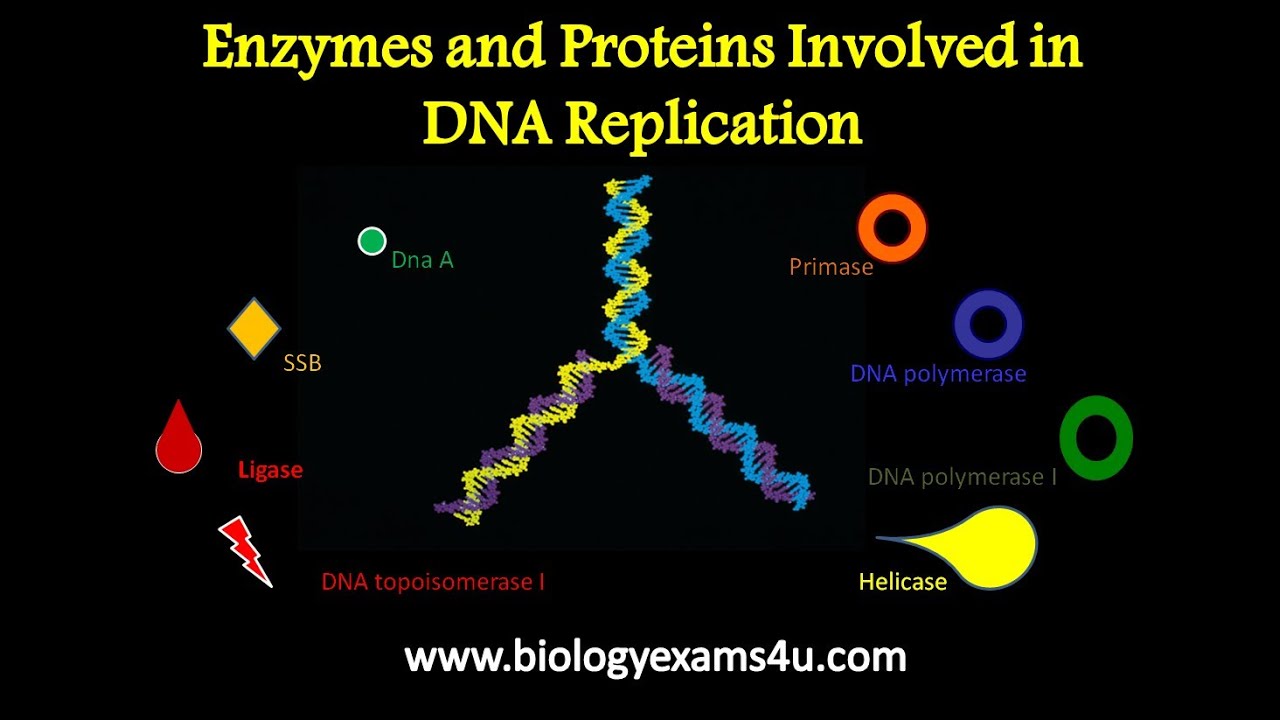
The enzymes involved in the process of DNA replication are as follows.
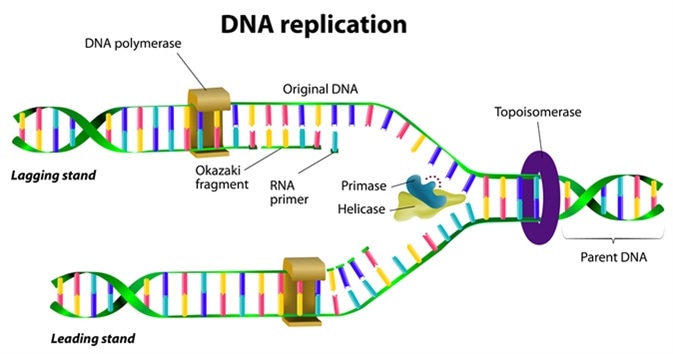
. The lagging strand begins replication by binding with multiple primers. Use the figure in part a and your knowledge of enzyme action and DNA replication to explain why new nucleotides can only be added in a 5 to 3 direction. Helicase that unwinds the double stranded DNA.
Other proteins are also involved for initiation of the process and copying of DNA along with proofreading capabilities to ensure the replication process takes place accurately. The enzymes involved in DNA replication are. DNA Polymerase III DNAP III.
Important Enzymes in DNA Replication. Prokaryotic DNA Polymerase. In eukaryotic cells polymerases alpha delta and epsilon are the primary polymerases involved in DNA replication.
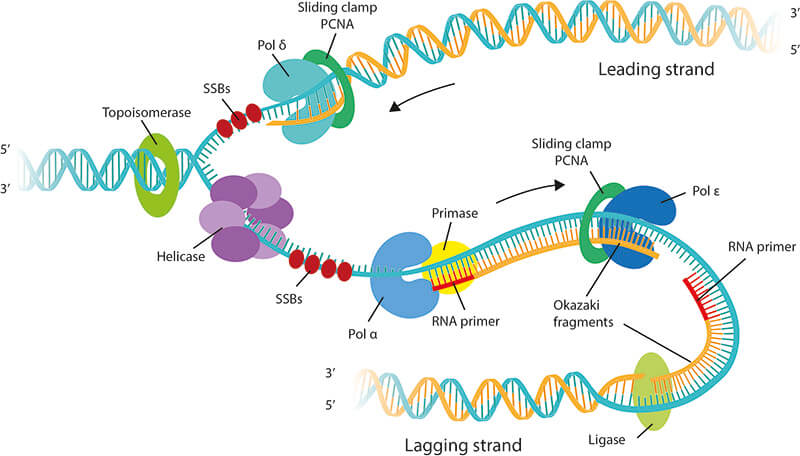
Let us discuss this in detail Single-Stranded Binding Protein SSBP DNA Helicases. This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together A with T C with G. Among them DNA-dependent DNA polymerase is the main enzyme.
These are special unwinding enzymes that help in breaking the weak hydrogen bonds which hold the two strands together. After catching up to previous primer DNA poly III must detach and move further into the fork after primase has added. These include 1 DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization.
Bind to the single strands of unwound DNA to prevent reformation of the DNA helix during replication. This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together A with T C with G. Single-Stranded Binding Protein SSBP SSBP means Single-Stranded Binding Proteins.
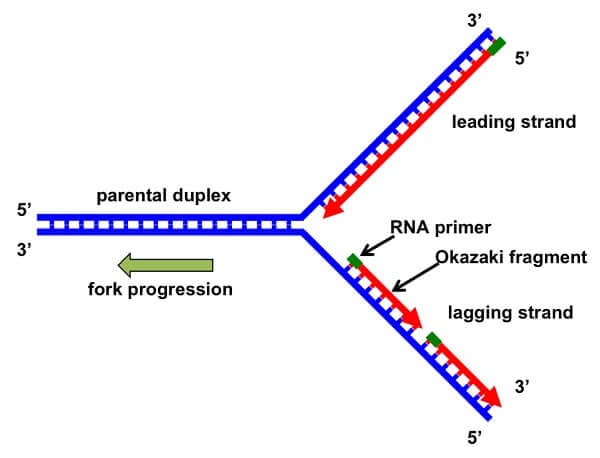
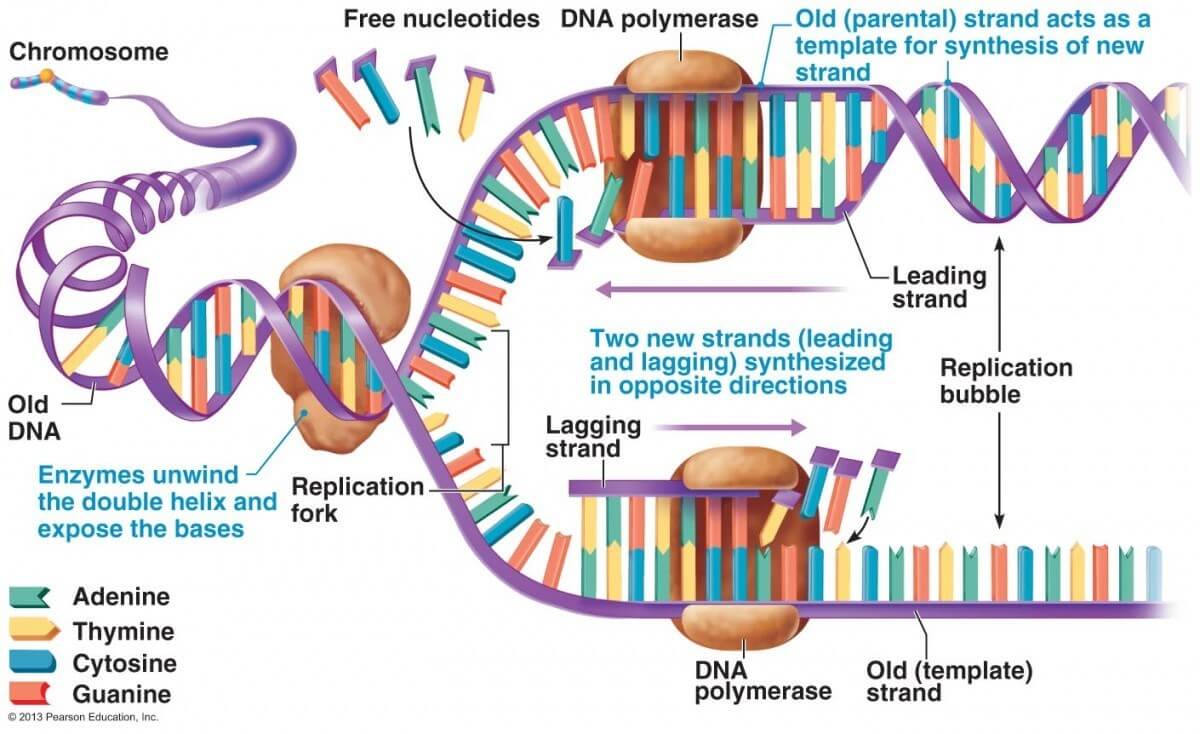
Synthesizes the RNA primer needed for the initiation of DNA chain synthesis. These two templates are used for replication. The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a Y shape called a replication fork.
Discuss the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell division and DNA replication. Provides the starting point for DNA polymerase to begin synthesis of the new strand. This is the list of Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication.
Explain what semiconservative DNA replication is and how it is different from conservative and dispersive models of DNA replication. 3 DNA ligase and an enzyme that degrades RNA primers to seal together the discontinuously synthesized lagging-strand DNA fragments. 2 DNA helicases and single-strand DNA-binding SSB proteins to help in opening up the DNA helix so that it can be copied.
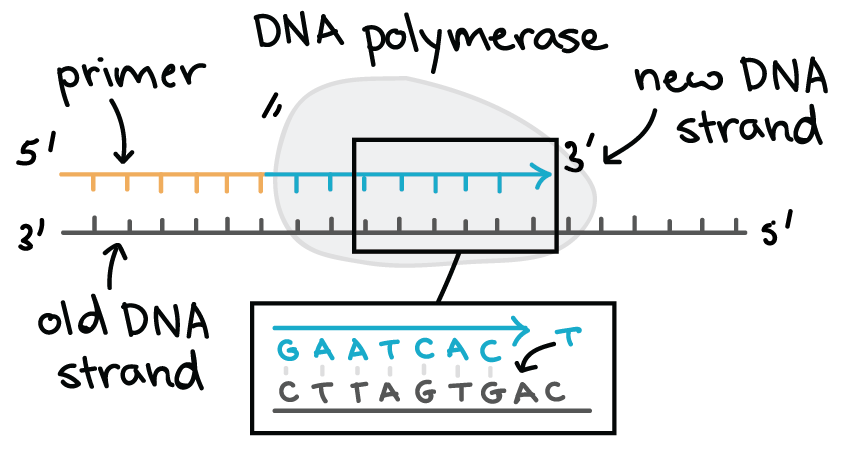
Because replication proceeds in the 5 to 3 direction on the leading strand the newly formed strand is continuous. DNA helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the double helix and exposes the two individual strands. The two separated strands will act.
Explain elongation stage of replication - your answer should include a discussion of leading strand lagging strand Okazaki pieces and RNA primer. DNA primase enzyme synthesises a small RNA primer that acts as a kick-starter for DNA polymerase. There are many enzymes involved in DNA replication which includes the enzymes DNA-dependent DNA polymerase helicase ligase etc.
DNA Replication Enzymes. Synthesizes the new DNA strand. Unwind the DNA helix at the start of replication.
Also proofreads and corrects some errors. Explain the role of enzymes in the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes. The first step in DNA replication is to unzip the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
Shapes of 5 end and 3 end are different description of how different. Primer adds primer near inside of fork DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides 5-3 moving away from fork. These primers are synthesized by DNA primase enzymes thus initiating the DNA replication process.
DNA polymerase that is involved in actual synthesis of DNA and brings nucleotides. Only complementary with binds to 5 end of strand. Name the five major enzymes involved in DNA replication and briefly explain their roles in the process.
Unwinds the double helix at the replication fork. It helps in the polymerisation catalyses and regularises the whole process of DNA replication with the support of other enzymes. DNA replication process uses DNA polymerase as the main enzyme for catalyzing the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs forming a growing chain of DNA.
These are the enzymes that can break and reseal one strand of DNA. Relaxes the super-coiled DNA. The enzyme DNA Helicase breaks the.
DNA polymerase creates the new strands of DNA and helps in its expansion. One of the most crucial enzymes is DNA Primase. For replication to occur each strand of DNA must be separated from the other a result of its double helix structure and the hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases.
Up to 256 cash back What is the order of enzymes in DNA replication. After the DNA strands are separated to begin the creation of new molecules through addition of complementary bases to the templates a short RNA segment called a primer is required. The first step in DNA replication is to unzip the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
A variety of enzymes are involved in the process of DNA replication. The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a Y shape called a replication fork. Enzymes of DNA Replication.

Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Enzymes And Proteins Involved In Dna Replication And Their Functions Youtube

Major Enzymes Biology For Majors I

Dna Replication Enzymes Order What Enzymes Are Used In Dna Replication Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii

Major Enzymes Biology For Majors I
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry
Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication
Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram
Dna Replication Study Guide Inspirit
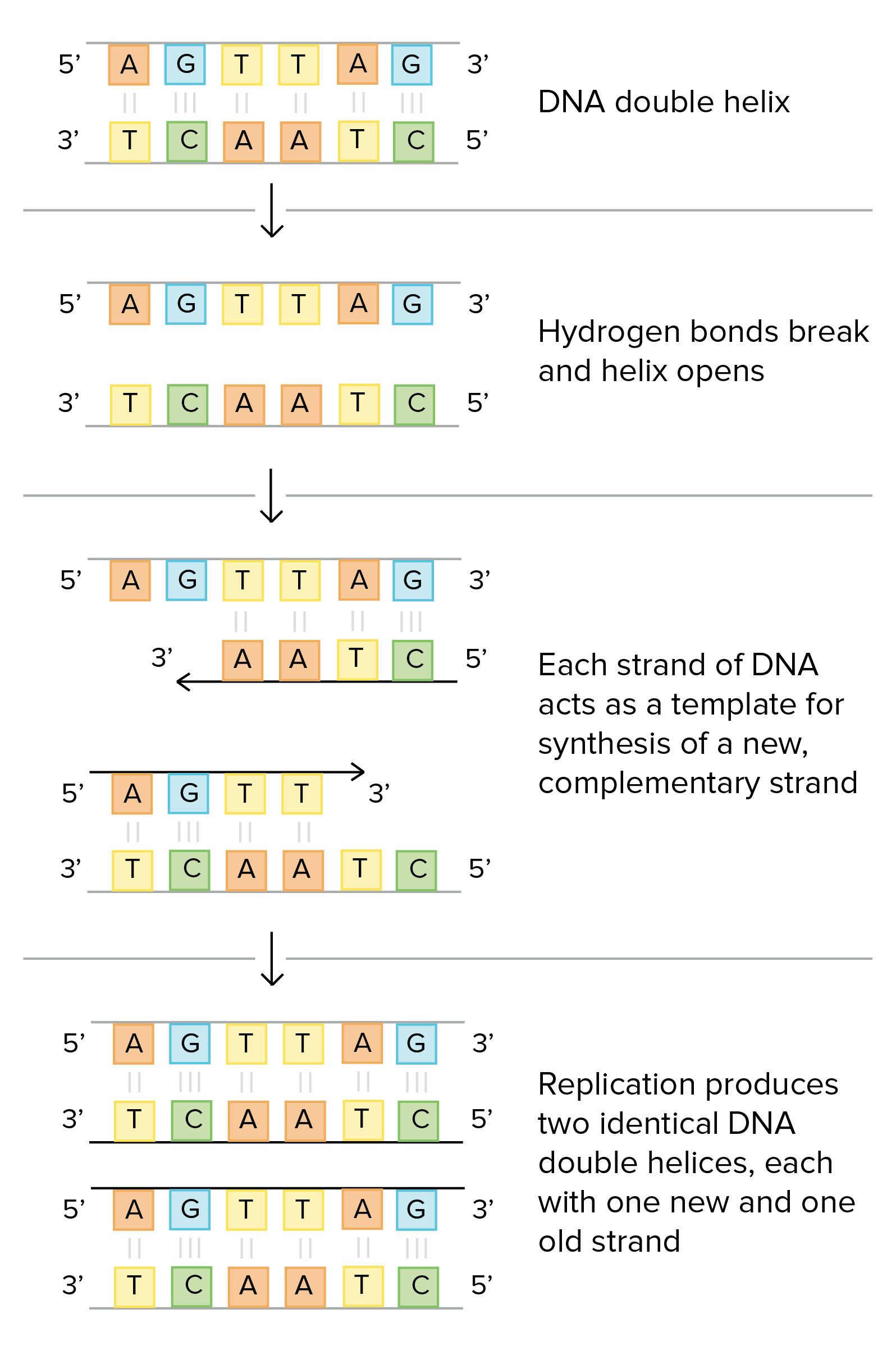
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
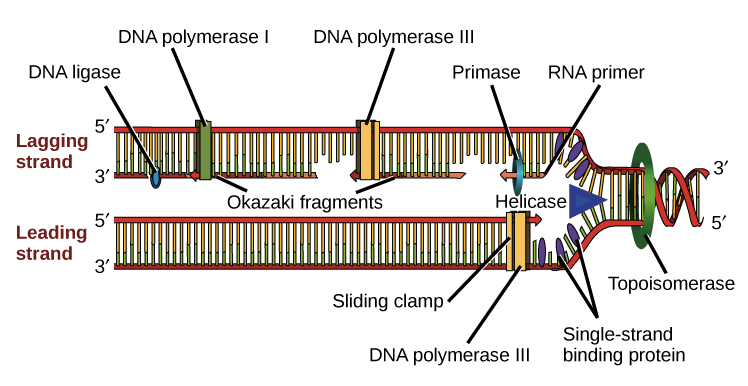
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
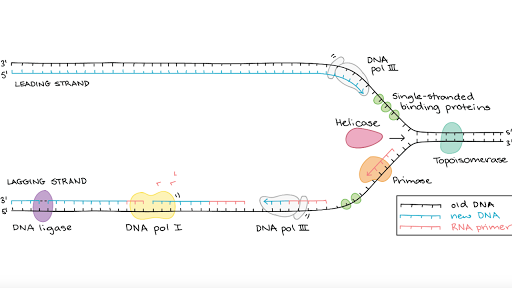
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy


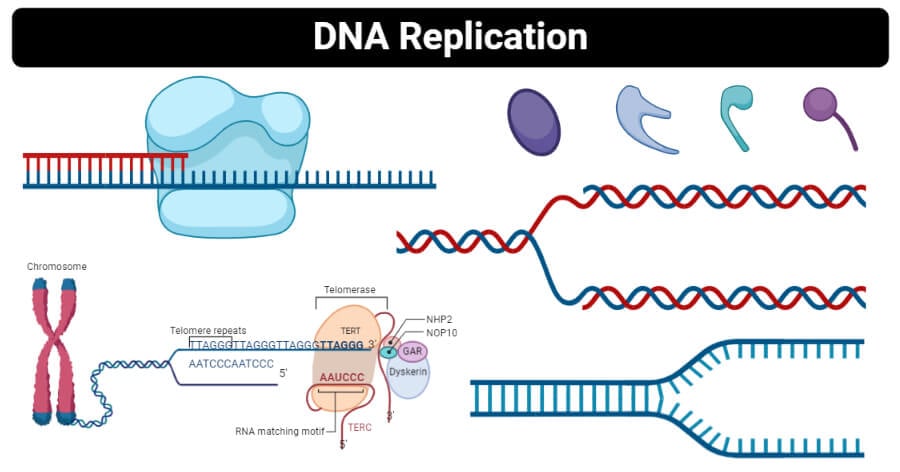
Comments
Post a Comment